Ansible 중급¶
이 문서에서는 계속해서 Ansible로 작업하는 방법을 배웁니다.
목적: 이 문서에서는 다음을 수행하는 방법에 대해 알아볼 것 입니다:
변수 작업하기
반복문(loop) 사용하기
상태 변경 관리 및 이에 대한 반응하기
비동기 작업을 관리하기
ansible, 모듈, 플레이북
지식:
복잡성:
소요 시간: 30분
이전 문서에서는 Ansible을 설치하는 방법, 명령줄에서 사용하는 방법 또는 코드 재사용성을 높이기 위해 플레이북을 작성하는 방법을 배웠습니다.
이 문서에서는 Ansible 용하는 더 고급된 개념과 자주 사용하는 흥미로운 작업 몇 가지를 알아볼 수 있습니다.
변수¶
참고
자세한 내용은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
Ansible에는 다음과 같은 다양한 유형의 기본 변수가 있습니다:
- 문자열
- 정수
- 부울값
이러한 변수는 다음과 같이 구성할 수 있습니다.
- 딕셔너리
- 리스트
예를 들어 플레이북, 역할 또는 명령줄과 같은 다양한 위치에서 변수를 정의할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 플레이북에서:
---
- hosts: apache1
vars:
port_http: 80
service:
debian: apache2
rhel: httpd
또는 명령줄에서:
$ ansible-playbook deploy-http.yml --extra-vars "service=httpd"
정의된 변수는 이중 중괄호 사이에서 호출하여 사용할 수 있습니다:
{{ port_http }}는 간단한 값에 대한 호출입니다.{{ service['rhel'] }}또는{{ service.rhel }}은 사전에 대한 호출입니다.
예를 들어:
- name: make sure apache is started
ansible.builtin.systemd:
name: "{{ service['rhel'] }}"
state: started
물론 Ansible의 전역 변수(facts)(OS 유형, IP 주소, VM 이름 등)에도 액세스할 수 있습니다.
변수 외부로 분리하기¶
변수는 플레이북과 별도로 외부 파일에 포함될 수 있으며, 이 경우 해당 파일은 vars_files 지시문으로 플레이북에서 정의해야 합니다:
---
- hosts: apache1
vars_files:
- myvariables.yml
myvariables.yml 파일:
---
port_http: 80
ansible.builtin.systemd::
debian: apache2
rhel: httpd
include_vars 모듈을 사용하여 동적으로 추가할 수도 있습니다.
- name: Include secrets.
ansible.builtin.include_vars:
file: vault.yml
변수 출력하기¶
변수를 출력하려면 다음과 같이 debug 모듈을 활성화해야 합니다.
- ansible.builtin.debug:
var: "{{ service['debian'] }}"
텍스트 내에서 변수를 사용할 수도 있습니다.
- ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Print a variable in a message : {{ service['debian'] }}"
작업 반환 저장¶
작업의 반환 값을 저장하고 나중에 액세스할 수 있도록하려면 작업 자체에서 키워드 register을 사용해야 합니다.
저장된 변수 사용:
- name: /home content
shell: ls /home
register: homes
- name: Print the first directory name
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: homes.stdout_lines[0]
- name: Print the first directory name
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: homes.stdout_lines[1]
참고
변수 homes.stdout_lines는 문자열 유형의 변수 리스트로, 우리가 이전에 만나지 못한 변수를 구성하는 방법입니다.
저장된 변수를 구성하는 문자열은 stdout값(homes.stdout.find("core") != -1과 같은 작업을 수행할 수 있음)을 통해 액세스하거나 루프(loop참조)를 사용하여 활용하거나 이전 예제에서 본 대로 인덱스를 사용하여 액세스할 수 있습니다.
연습 문제¶
대상의 배포판 이름과 주요 버전을 출력하는 플레이북
play-vars.yml을 작성하십시오. 이를 위해 전역 변수를 사용하세요.다음 사전을 사용하여 설치될 서비스를 표시하는 playbook을 작성하세요:
service:
web:
name: apache
rpm: httpd
db:
name: mariadb
rpm: mariadb-server
기본 유형은 "web"이어야 합니다.
명령줄을 사용하여
type변수 재정의하세요.vars.yml파일에서 변수 외부화하세요.
루프 관리¶
루프를 사용하면 예를 들어 목록, 해시 또는 사전에 대해 작업을 반복할 수 있습니다.
참고
자세한 내용은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
4개의 사용자를 만드는 간단한 사용 예제:
- name: add users
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
groups: "users"
loop:
- antoine
- patrick
- steven
- xavier
루프의 각 반복에서 사용되는 리스트의 값은 item 변수에 저장되어 루프 코드에서 액세스할 수 있습니다.
물론, 리스트는 외부 파일에 정의될 수 있습니다:
users:
- antoine
- patrick
- steven
- xavier
그리고 다음과 같이 작업 내에서 사용할 수 있습니다 (변수 파일을 포함한 후):
- name: add users
user:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: present
groups: "users"
loop: "{{ users }}"
저장된 변수를 연구하는 동안 본 예제를 사용하여 개선할 수 있습니다. 저장된 변수 사용:
- name: /home content
shell: ls /home
register: homes
- name: Print the directories name
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "Directory => {{ item }}"
loop: "{{ homes.stdout_lines }}"
루프에서도 사전을 사용할 수 있습니다.
이 경우 jinja filter(jinja는 Ansible에서 사용하는 템플릿 엔진)를 사용하여 사전을 항목으로 변환해야 합니다: | dict2items.
루프에서 사전 키에 해당하는 item.key와 키 값에 해당하는 item.value를 사용할 수 있게 됩니다.
시스템 사용자 관리를 보여주는 구체적인 예를 통해 이를 살펴보겠습니다.
---
- hosts: rocky8
become: true
become_user: root
vars:
users:
antoine:
group: users
state: present
steven:
group: users
state: absent
tasks:
- name: Manage users
user:
name: "{{ item.key }}"
group: "{{ item.value.group }}"
state: "{{ item.value.state }}"
loop: "{{ users | dict2items }}"
참고
루프를 사용하여 많은 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다. Ansible을 사용하여 루프를 더 복잡한 방식으로 사용하게 되면 루프가 제공하는 가능성을 발견하게 될 것입니다.
연습 문제¶
- 이전 연습에서 작성한
service변수의 내용을 루프를 사용하여 표시하세요.
참고
service 변수를 사전에서 리스트로 변환해야 합니다. 이를 위해 다음과 같이 jinja 필터 list를 사용하세요:
{{ service.values() | list }}
조건부¶
참고
자세한 내용은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
when 문은 많은 경우에 매우 유용합니다. 특정 유형의 서버에서 특정 작업을 수행하지 않거나 파일이나 사용자가 존재하지 않을 경우 등을 처리할 수 있습니다.
참고
when 문 뒤에는 변수에 이중 중괄호가 필요하지 않습니다(사실 Jinja2 표현식입니다...).
- name: "Reboot only Debian servers"
reboot:
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
조건은 괄호로 그룹화할 수 있습니다.
- name: "Reboot only CentOS version 6 and Debian version 7"
reboot:
when: (ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "6") or
(ansible_distribution == "Debian" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "7")
논리 AND에 해당하는 조건을 목록으로 제공할 수 있습니다.
- name: "Reboot only CentOS version 6"
reboot:
when:
- ansible_distribution == "CentOS"
- ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
boolean값을 테스트하고 true인지 확인할 수도 있습니다:
- name: check if directory exists
stat:
path: /home/ansible
register: directory
- ansible.builtin.debug:
var: directory
- ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: The directory exists
when:
- directory.stat.exists
- directory.stat.isdir
true가 아닌지도 테스트할 수 있습니다:
when:
- file.stat.exists
- not file.stat.isdir
실행 오류를 피하기 위해 변수가 존재하는지 테스트해야 할 것입니다.
when: myboolean is defined and myboolean
연습 문제¶
type이web과 같은 경우에만service.web의 값을 출력하세요.
변경 관리: 핸들러¶
참고
자세한 내용은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
핸들러를 사용하면 변경 사항이 발생할 때 서비스를 다시 시작하는 등의 작업을 실행할 수 있도록 해줍니다.
모듈은 멱등성을 가지므로 playbook은 원격 시스템에서 중대한 변경 사항이 발생했음을 감지하고 이 변경에 대한 반응으로 작업을 트리거할 수 있습니다. 알림은 playbook 작업 블록의 끝에 전송되며, 여러 작업에서 동일한 알림을 보내더라도 반응 작업은 한 번만 트리거됩니다.
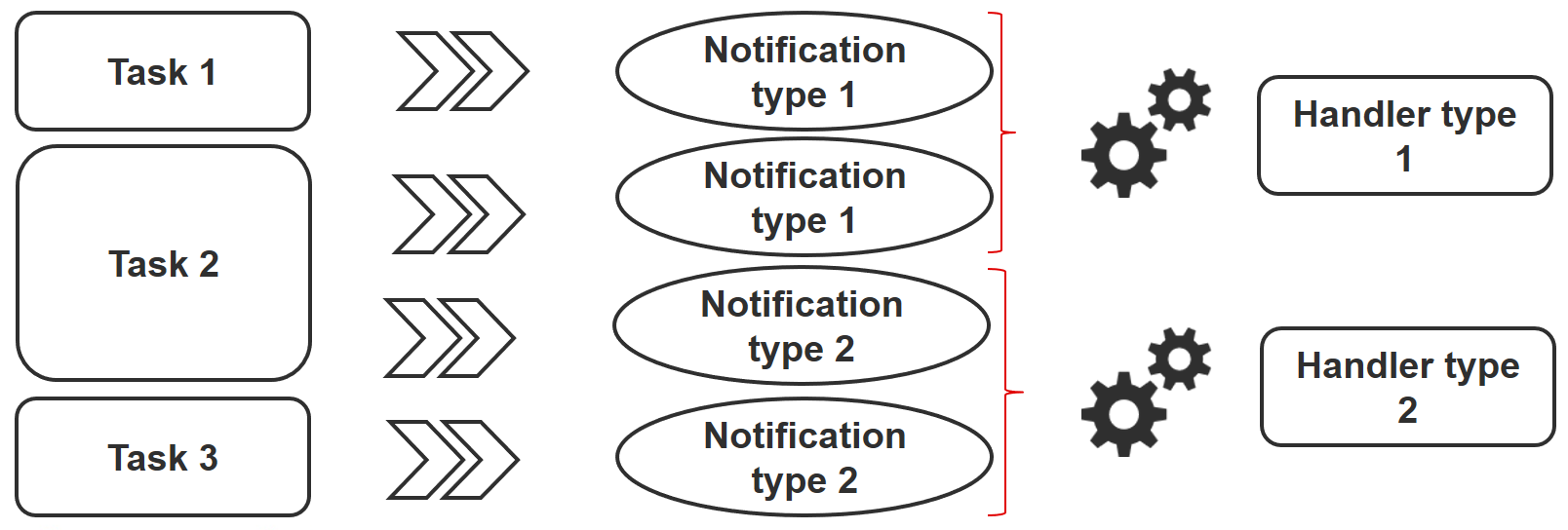
예를 들어 여러 작업에서 구성 파일의 변경으로 인해 httpd 서비스를 다시 시작해야 함을 나타낼 수 있습니다. 그러나 중복되는 불필요한 시작을 피하기 위해 서비스는 한 번만 다시 시작됩니다.
- name: template configuration file
template:
src: template-site.j2
dest: /etc/httpd/sites-availables/test-site.conf
notify:
- restart memcached
- restart httpd
핸들러는 고유한 전역 이름으로 참조되는 일종의 작업입니다:
- 하나 이상의 알림 기능에 의해 활성화됩니다.
- 즉시 시작되지 않고 모든 작업이 완료될 때까지 대기합니다.
핸들러의 예시:
handlers:
- name: restart memcached
systemd:
name: memcached
state: restarted
- name: restart httpd
systemd:
name: httpd
state: restarted
Ansible 버전 2.2부터 핸들러도 직접 수신할 수 있습니다.
handlers:
- name: restart memcached
systemd:
name: memcached
state: restarted
listen: "web services restart"
- name: restart apache
systemd:
name: apache
state: restarted
listen: "web services restart"
tasks:
- name: restart everything
command: echo "this task will restart the web services"
notify: "web services restart"
비동기 작업¶
참고
자세한 내용은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
기본적으로 호스트로의 SSH 연결은 모든 노드에서 여러 playbook 작업이 실행되는 동안 열려 있는 상태로 유지됩니다.
이는 몇 가지 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 특히 다음과 같은 경우에:
- 작업의 실행 시간이 SSH 연결 시간 초과보다 길 때
- 동작 중에 연결이 중단되는 경우(예: 서버 재부팅)
이 경우 비동기 모드로 전환하고 최대 실행 시간과 호스트 상태를 확인할 빈도(기본값 10초)를 지정해야 합니다.
poll 값에 0을 지정하면 Ansible은 작업을 실행하고 결과를 걱정하지 않고 계속 진행합니다.
다음은 비동기 작업을 사용하는 예제로, 서버를 재시작하고 포트 22가 다시 사용 가능해질 때까지 대기하는 것을 허용합니다:
# 2초 기다린 후 재부팅 시작
- name: Reboot system
shell: sleep 2 && shutdown -r now "Ansible reboot triggered"
async: 1
poll: 0
ignore_errors: true
become: true
changed_when: False
# 서버가 사용 가능할 때까지 기다립니다.
- name: Waiting for server to restart (10 mins max)
wait_for:
host: "{{ inventory_hostname }}"
port: 22
delay: 30
state: started
timeout: 600
delegate_to: localhost
또한 플레이북에서 실행이 중요하지 않기 때문에 장기간 실행 중인 작업을 시작하고 잊어버리도록 결정할 수도 있습니다.
연습 결과¶
play-vars.yml파일을 작성하여 대상의 배포 이름과 주요 버전을 전역 변수를 사용하여 출력하는 플레이북을 작성하세요.
---
- hosts: ansible_clients
tasks:
- name: Print globales variables
debug:
msg: "The distribution is {{ ansible_distribution }} version {{ ansible_distribution_major_version }}"
$ ansible-playbook play-vars.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print globales variables] ************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => {
"msg": "The distribution is Rocky version 8"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
- 다음 사전을 사용하여 설치될 서비스를 표시하는 playbook을 작성하세요:
service:
web:
name: apache
rpm: httpd
db:
name: mariadb
rpm: mariadb-server
기본 유형은 "web"이어야 합니다.
---
- hosts: ansible_clients
vars:
type: web
service:
web:
name: apache
rpm: httpd
db:
name: mariadb
rpm: mariadb-server
tasks:
- name: Print a specific entry of a dictionary
debug:
msg: "The {{ service[type]['name'] }} will be installed with the packages {{ service[type].rpm }}"
$ ansible-playbook display-dict.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a specific entry of a dictionnaire] ********************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => {
"msg": "The apache will be installed with the packages httpd"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
- 명령줄을 사용하여
type변수를 재정의합니다:
ansible-playbook --extra-vars "type=db" display-dict.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a specific entry of a dictionary] ********************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => {
"msg": "The mariadb will be installed with the packages mariadb-server"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
vars.yml파일에서 변수 외부화하세요.
type: web
service:
web:
name: apache
rpm: httpd
db:
name: mariadb
rpm: mariadb-server
---
- hosts: ansible_clients
vars_files:
- vars.yml
tasks:
- name: Print a specific entry of a dictionary
debug:
msg: "The {{ service[type]['name'] }} will be installed with the packages {{ service[type].rpm }}"
- 이전 연습에서 작성한
service변수의 내용을 루프를 사용하여 표시하세요.
참고
service 변수를 item이나 list와 함께 jinja 필터 dict2items 또는 list를 사용하여 사전에서 항목 또는 목록으로 변환해야 합니다.
{{ service | dict2items }}
{{ service.values() | list }}
dict2items 사용한 경우:
---
- hosts: ansible_clients
vars_files:
- vars.yml
tasks:
- name: Print a dictionary variable with a loop
debug:
msg: "{{item.key }} | The {{ item.value.name }} will be installed with the packages {{ item.value.rpm }}"
loop: "{{ service | dict2items }}"
$ ansible-playbook display-dict.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a dictionary variable with a loop] ********************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => (item={'key': 'web', 'value': {'name': 'apache', 'rpm': 'httpd'}}) => {
"msg": "web | The apache will be installed with the packages httpd"
}
ok: [192.168.1.11] => (item={'key': 'db', 'value': {'name': 'mariadb', 'rpm': 'mariadb-server'}}) => {
"msg": "db | The mariadb will be installed with the packages mariadb-server"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
list를 사용한 경우:
---
- hosts: ansible_clients
vars_files:
- vars.yml
tasks:
- name: Print a dictionary variable with a loop
debug:
msg: "The {{ item.name }} will be installed with the packages {{ item.rpm }}"
loop: "{{ service.values() | list}}"
~
$ ansible-playbook display-dict.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a dictionary variable with a loop] ********************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => (item={'name': 'apache', 'rpm': 'httpd'}) => {
"msg": "The apache will be installed with the packages httpd"
}
ok: [192.168.1.11] => (item={'name': 'mariadb', 'rpm': 'mariadb-server'}) => {
"msg": "The mariadb will be installed with the packages mariadb-server"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
type이web과 같은 경우에만service.web의 값을 출력하세요.
---
- hosts: ansible_clients
vars_files:
- vars.yml
tasks:
- name: Print a dictionary variable
debug:
msg: "The {{ service.web.name }} will be installed with the packages {{ service.web.rpm }}"
when: type == "web"
- name: Print a dictionary variable
debug:
msg: "The {{ service.db.name }} will be installed with the packages {{ service.db.rpm }}"
when: type == "db"
$ ansible-playbook display-dict.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a dictionary variable] ********************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => {
"msg": "The apache will be installed with the packages httpd"
}
TASK [Print a dictionary variable] ********************************************************************
skipping: [192.168.1.11]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0
$ ansible-playbook --extra-vars "type=db" display-dict.yml
PLAY [ansible_clients] *********************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a dictionary variable] ********************************************************************
skipping: [192.168.1.11]
TASK [Print a dictionary variable] ********************************************************************
ok: [192.168.1.11] => {
"msg": "The mariadb will be installed with the packages mariadb-server"
}
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************************************
192.168.1.11 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=1 rescued=0 ignored=0