Introduction¶
Podman is a Docker-compatible alternative container runtime that, unlike Docker, is included in the Rocky Linux repositories and can run containers as a systemd service.
Install Podman¶
Use the dnf utility to install Podman:
dnf install podman
Adding a container¶
Let us run a Nextcloud self-hosted cloud platform as an example:
podman run -d -p 8080:80 nextcloud
You will receive a prompt to select the container registry from which to download. In our example, we will use docker.io/library/nextcloud:latest.
Once you have downloaded the Nextcloud container, it will run.
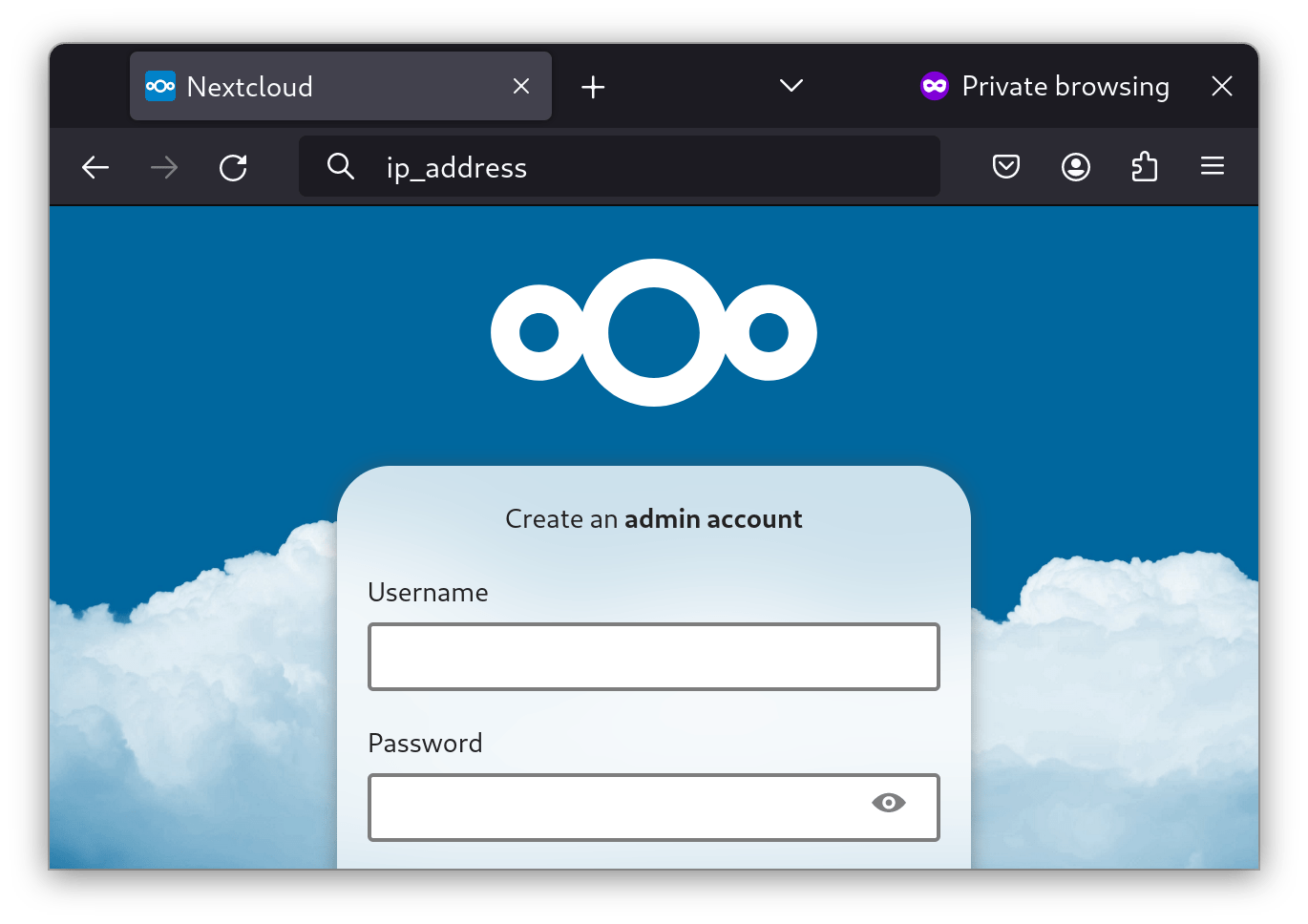
Enter ip_address:8080 in your web browser (assuming you opened the port in firewalld) and set up Nextcloud:
Running containers as systemd services¶
Using quadlet¶
Since 4.4, Podman ships with Quadlet, a systemd generator that can generate unit files for rootless and rootful systemd services.
Quadlet files for rootful services can be placed in
/etc/containers/systemd//usr/share/containers/systemd/
while rootless files can be placed in either of
$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/containers/systemd/or~/.config/containers/systemd//etc/containers/systemd/users/$(UID)/etc/containers/systemd/users/
While single containers, pods, images, networks, volumes, and kube files are supported, let's focus on our Nextcloud example. Create a new file ~/.config/containers/systemd/nextcloud.container with the following content:
[Container]
Image=nextcloud
PublishPort=8080:80
A lot of other options are available.
To run the generator and let systemd know that there is a new service run:
systemctl --user daemon-reload
To now run your service run:
systemctl --user start nextcloud.service
Note
If you created a file in one of the directories for rootful services, omit the --user flag.
To automatically run the container upon system start or user login, you can add another section to your nextcloud.container file:
[Install]
WantedBy=default.target
As the generated service files are considered transient, they cannot be enabled by systemd. To mitigate this, the generator manually applies installs during generation. This effectively also enables those services files.
Other file types are supported: pod, volume, network, image, and kube. Pods, for instance, can be used to group containers – the generated systemd services and their dependencies (create the pod before the containers) are automatically managed by systemd.
Using podman generate systemd¶
Podman additionally provides the generate systemd subcommand. It can be used to generate systemd service files.
Warning
generate systemd is now deprecated and will not receive further features. The usage of Quadlet is recommended.
Let us now do it with Nextcloud. Run:
podman ps
You will get a list of running containers:
04f7553f431a docker.io/library/nextcloud:latest apache2-foregroun... 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp compassionate_meninsky
As seen above, our container's name is compassionate_meninsky.
To make a systemd service for the Nextcloud container and enable it on reboot, run the following:
podman generate systemd --name compassionate_meninsky > /usr/lib/systemd/system/nextcloud.service
systemctl enable nextcloud
Replace compassionate_meninsky with your container's assigned name.
When your system reboots, Nextcloud will restart in Podman.
Author: Neel Chauhan
Contributors: Steven Spencer, Ganna Zhyrnova, Christian Steinert